Advertisement
Art and technology have always had a curious relationship. Now, that relationship is evolving into something surprisingly creative and collaborative. When it comes to sketch generation, the story is no different. The rise of deep learning models has made it possible to create impressive sketches from scratch, and one model, in particular, is getting all the attention: DCGAN. It stands for Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network, and it’s taking creative sketch generation to a completely new place. Let’s look at how this works and why so many artists, developers, and researchers are excited.
DCGAN is founded on a straightforward yet intriguing premise: two neural networks competing with one another to improve with time. One network generates images (the generator), whereas the other attempts to detect forgeries (the discriminator). With each challenge to one another, both of them get better. For sketch generation, this competition results in sketches that become more realistic, full of texture, and heavy with detail.
Traditionally, sketch generation involved either manually drawing or using basic computer programs that couldn’t capture the subtlety of human lines. But DCGAN does something different. It learns directly from thousands of real sketches, identifying patterns humans might not even notice, and then uses that knowledge to create something brand new. Instead of copying, it imagines — and the results can be both surprising and beautiful.
Researchers first showed the world what DCGAN could do in 2015, and since then, artists and engineers have found ways to fine-tune it for different creative tasks. Whether it’s creating portraits, fashion designs, or fantasy landscapes, DCGAN has proven itself to be a tool that can think outside the box.
If you’re curious about the nuts and bolts, it’s pretty clever. DCGAN uses layers of convolution — the same thing your brain does when it processes what you see. Early layers might detect simple edges, like where a line begins or ends. Later layers recognize shapes, textures, and full forms. Every piece of information moves through the network, helping it build a more complete picture of what a good sketch should look like.
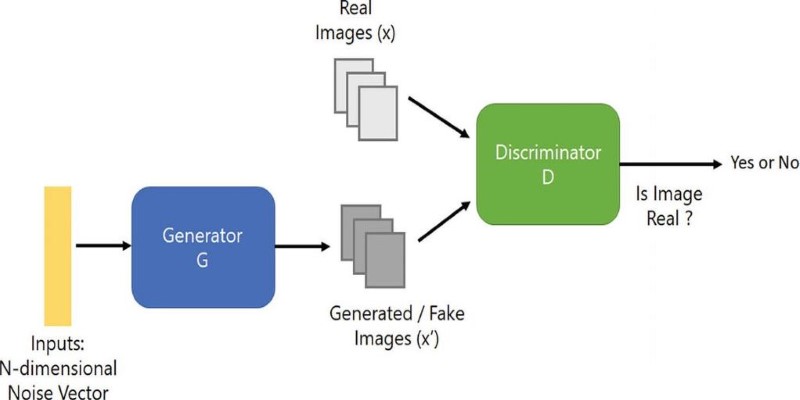
Training a DCGAN model usually involves a large dataset of real sketches. The generator starts by producing random noise. It's ugly at first — just scribbles. The discriminator easily calls it out as fake. But over time, the generator adjusts. It learns the style, shading, proportions, and flow that makes a drawing feel real. Eventually, the generator can produce a sketch so believable that even the discriminator struggles to tell if it's computer-made or drawn by a person.
It's not magic, but it feels close. What's especially exciting is that DCGAN doesn't just reproduce existing sketches. It finds new combinations, blending elements it learned and offering fresh designs no one has ever seen before.
You might be wondering — where is this technology actually used? The answer is almost everywhere: creative thinking meets technology.
Character and Game Design
In video game development, designers often spend weeks sketching characters, weapons, environments, and more. DCGAN can speed up the early concept stages by providing dozens of original sketches in minutes. Artists can then pick and refine the best ones instead of starting from scratch.
Fashion and Industrial Design
Fashion designers are using DCGAN to experiment with new clothing sketches, patterns, and even accessories. Similarly, industrial designers apply it to quickly generate ideas for products like furniture, electronics, and tools, giving them a wider creative pool to work with.
Education and Learning Tools
Some educators are experimenting with DCGAN models to teach art students about styles, shading, and proportions. By analyzing thousands of sketches and offering examples, the models help students see what defines a great sketch without needing hours of manual review.
Assisting People with Disabilities
For individuals who have a passion for drawing but find it physically difficult, DCGAN can offer support by helping them create sketches with minimal input. Whether it's controlling the generator through voice commands or simple gestures, creative expression becomes more accessible.
While DCGAN has already made a big splash, it’s not without its limits. One challenge is that it can sometimes produce sketches that feel too “perfect” or mechanical. The tiny mistakes, hesitations, and quirks that give a human-made sketch its charm are not always easy for a machine to copy.

Another issue is training bias. If the dataset mostly features a certain type of sketch — say, realistic portraits — then the DCGAN might struggle when asked to produce something more abstract or playful. So, artists and developers have to be careful about the examples they feed into the model.
What's next for creative sketch generation looks exciting. Newer versions of GANs are working on capturing finer details, handling multiple styles at once, and even reacting in real time to user feedback. Some researchers are combining DCGAN with other models like VAE (Variational Autoencoder) to offer more control over the output, letting artists tweak style, mood, or even the number of strokes used in a sketch.
Another promising direction is lightweight DCGAN models that run on smartphones or tablets. Imagine opening an app, describing what you want to sketch, and getting a selection of ready-to-edit drawings within seconds.
DCGAN has reshaped the way people think about creative sketch generation. With its ability to learn from real-world art and produce original sketches, it’s making the creative process faster, broader, and more exciting. Whether you’re an artist looking for inspiration, a designer racing against deadlines, or simply someone curious about what machines can create, DCGAN is offering a glimpse into a future where creativity and technology walk hand in hand. And from what we’ve seen so far, that future looks pretty amazing.
Advertisement

Which RAG tools are worth your time for generative AI? This guide breaks down the top options and shows you how to get started with the right setup
Curious about where AI is headed after ChatGPT? Take a look at what's coming next in the world of generative AI and how chatbots might evolve in the near future

Discover 10 ChatGPT plugins designed to simplify PDF tasks like summarizing, converting, creating, and extracting text.

Looking for the best way to start learning data science without getting lost? Here are 9 beginner-friendly coding platforms that make it easy to begin and stay on track

Which machine learning tools actually help get real work done? This guide breaks down 9 solid options and shows you how to use PyTorch with clarity and control

Veed.io makes video editing easy and fast with AI-powered tools. From auto-generated subtitles to customizable templates, create professional videos without hassle

Curious how machines are learning to create original art? See how DCGAN helps generate realistic sketches and brings new ideas to creative fields

How can AI help transform your sketches into realistic renders? Discover how PromeAI enhances your designs, from concept to portfolio-ready images, with ease and precision

Looking for the best places to buy or sell AI prompts? Discover the top AI prompt marketplaces of 2025 and find the right platform to enhance your AI projects

Looking for smarter ways to code in 2025? These AI coding assistants can help you write cleaner, faster, and more accurate code without slowing you down

Need help setting up Microsoft Copilot on your Mac? This step-by-step guide walks you through installation and basic usage so you can start working with AI on macOS today.

Discover how AI and DevOps team up to boost remote work with faster delivery, smart automation, and improved collaboration